How do human beings process sentences so rapidly?
- Finite State Devices
The ¡ old ¡ man ¡ likes ¡ John art: the adj: old noun: man verb: likes noun: John DEF OLD MAN LIKES PN: ID - Problems for Finite State Devices .
- Recursivity
the old man who reads books that are popular likes John
Solution: Separate N, V, A, det, aux, p processors - Movement: It's John the old man likes? Does the old man
like John?
Solution: separate phrase types - Ambiguity: The horse ran past the barn fell (garden-path sentences)
- Lexical encoding
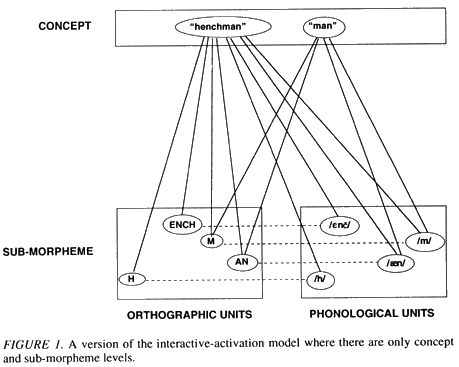
- polysemy: dope,
- synonymy: sofa : couch, bag : sack, bucket : pail
- homophony: pear, pare, pair
- polycategoriality: fire, hammer, rose, cooler
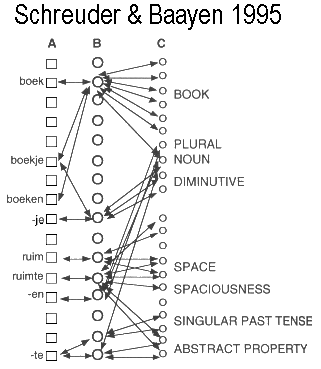
Figure 2. Access representations (layer A); concept nodes (layer B); semantic and syntactic nodes (layer C); and their connections for the Dutch noun boek 'book,' the adjective ruim 'spacious,' and related inflected and derived complex forms.
- Schemas / Scripts
- a set of expectations
- The waiter . . . .
- The fire hydrant . . . .
- The family cat . . . .
- Spreading Activation Network
RESTAURANT script
maitre d'hotel  show
to table
show
to table give
menu
give
menu expect
tip
expect
tiptable  chair
chair
 legs
legs
 back
back

 spine
spine

 upright
upright

 lean
back
lean
back
table cloth 
flowers 
salt & pepper 
sugar waiter  take
order
take
order

 a
la carte
a
la carte
 complete
dinner
complete
dinner
 luncheon
menu
luncheon
menu
 breakfast
menu
breakfast
menu
 ask
about water
ask
about water
 bring
order
bring
order tip
tip

 15%
15%
 leave
on table
leave
on table complain
to
complain
to
- a set of expectations
- Ambiguity (Why do we make the processing errors we do and not those
we don't? )
- The firm drives . . . .
- The British left waffles [on the Falkland Islands]
- Garden path sentencesThe horse walked past the barn fell.
Conclusions??