Ukraine


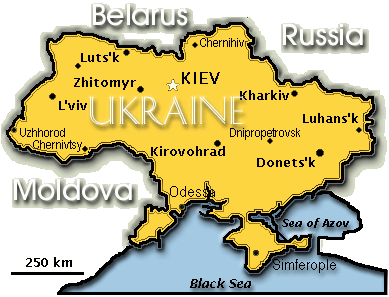
Geography
Location: Eastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, between Poland and RussiaArea:
total area: 603,700 sq km
land area: 603,700 sq km
comparative area: slightly smaller than TexasLand boundaries: total 4,558 km, Belarus 891 km, Hungary 103 km, Moldova 939 km, Poland 428 km, Romania (southwest) 169 km, Romania (west) 362 km, Russia 1,576 km, Slovakia 90 km
Coastline: 2,782 km
Maritime claims: NA
International disputes: potential future border disputes with Moldova and Romania in Northern Bukovina and southern Odes'ka Oblast'; potential dispute with Moldova over former southern Bessarabian area; potential dispute with Russia over Crimea; has made no territorial claim in Antarctica (but has reserved the right to do so) and does not recognize the claims of any other nation
Climate: temperate continental; subtropical only on the southern Crimean coast; precipitation disproportionately distributed, highest in west and north, lesser in east and southeast; winters vary from cool along the Black Sea to cold farther inland; summers are warm across the greater part of the country, hot in the south
Terrain: most of Ukraine consists of fertile plains (steppes) and plateaux, mountains being found only in the west (the Carpathians), and in the Crimean Peninsula in the extreme south
Natural resources: iron ore, coal, manganese, natural gas, oil, salt, sulphur, graphite, titanium, magnesium, kaolin, nickel, mercury, timber
Land use:
arable land: 56%
permanent crops: 2%
meadows and pastures: 12%
forest and woodland: 0%
other: 30%Irrigated land: 26,000 sq km (1990)
Environment:
current issues : unsafe drinking water; air and water pollution; deforestation; radiation contamination in the northeast from 1986 accident at Chornobyl' Nuclear Power Plant
natural hazards: NA
international agreements: party to - Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur, Antarctic Treaty, Environmental Modification, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution; signed, but not ratified - Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Law of the SeaNote: strategic position at the crossroads between Europe and Asia; second largest country in Europe
People
Who's Who in UkrainePopulation: 51,846,958 (July 1994 est.)
Population growth rate: 0.05% (1994 est.)
Birth rate: 12.34 births/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Death rate: 12.6 deaths/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Net migration rate: 0.71 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 20.7 deaths/1,000 live births (1994 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 69.99 years
male: 65.45 years
female : 74.76 years (1994 est.)Total fertility rate: 1.82 children born/woman (1994 est.)
Nationality:
noun : Ukrainian(s)
adjective: UkrainianEthnic divisions: Ukrainian 73%, Russian 22%, Jewish 1%, other 4%
Religions: Ukrainian Orthodox - Moscow Patriarchate, Ukrainian Orthodox - Kiev Patriarchate, Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox, Ukrainian Catholic (Uniate), Protestant,Jewish
Languages: Ukrainian, Russian, Romanian, Polish, Hungarian
Literacy: age 9-49 can read and write (1979)
total population: 100%
male: 100%
female: 100%Labor force: 23.985 million
by occupation: industry and construction 33%, agriculture and forestry 21%, health, education, and culture 16%, trade and distribution 7%, transport and communication 7%, other 16% (1992)
Government
Names:
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Ukraine
local long form: none
local short form: Ukrayina
former: Ukrainian Soviet Socialist RepublicDigraph: UP
Type: republic
Capital: Kiev (Kyyiv)
Administrative divisions: 24 oblasti (singular - oblast'), 1 autonomous republic* (avtomnaya respublika), and 2 municipalites (mista, singular - misto) with oblast status**; Cherkas'ka (Cherkasy), Chernihivs'ka (Chernihiv), Chernivets'ka (Chernitsi), Dnipropetrovs'ka (Dnipropetrovs'k), Donets'ka (Donets'k), Ivano-Frankivs'ka (Ivano-Frankivs'k), Kharkivs'ka (Kharkiv), Khersons'ka (Kherson), Khmel'nyts'ka (Khmel'nyts'kyy), Kirovohrads'ka (Kirovohrad), Kyyiv**, Kyyivs'ka (Kiev), Luhans'ka (Luhans'k), L'vivs'ka (L'viv), Mykolayivs'ka (Mykolayiv), Odes'ka (Odesa), Poltavs'ka (Poltava), Respublika Krym* (Simferopol'), Rivnens'ka (Rivne), Sevastopol'**,Sums'ka (Sevastopol'), Ternopil's'ka (Ternopil'), Vinnyts'ka (Vinnytsya), Volyns'ka (Luts'k), Zakarpats'ka (Uzhhorod), Zaporiz'ka (Zaporizhzhya), Zhytomyrs'ka (Zhytomyr)
note: names in parentheses are administrative centers when name differs from oblast' nameIndependence: 1 December 1991 (from Soviet Union)
National holiday: Independence Day, 24 August (1991)
Constitution: using 1978 pre-independence constitution; new constitution currently being drafted
Legal system: based on civil law system; no judicialreview of legislative acts
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: President-elect Leonid D. KUCHMA; election last held 26 June and 10 July 1994 (next to be held NA 1999); results - Leonid KUCHMA 52.15%, Leonid KRAVCHUK 45.06%
head of government: Prime Minister (vacant); Acting First Deputy Prime Minister (and Acting Prime Minister since September 1993) Yukhym Leonidovych ZVYAHIL'SKYY (since 11 June 1993) and five deputy prime ministers
cabinet: Council of Ministers; appointed by the president and approved by the Supreme CouncilLegislative branch: unicameral
Supreme Council (Verkhovna Rada): elections last held 27 March 1994 (next to be held NA); results - percent of vote by party NA; seats - (450 total) number of seats by party NA; note - 338 deputies were elected; the remaining 112 seats to be filled on 24 July 1994Judicial branch: being organized
Political parties and leaders: Green Party of Ukraine, Vitaliy KONONOV, leader; Liberal Party of Ukraine, Ihor MERKULOV, chairman; Liberal Democratic Party of Ukraine, Volodymyr KLYMCHUK, chairman; Democratic Party of Ukraine, Volodymyr Oleksandrovych YAVORIVSKIY, chairman; People's Party of Ukraine, Leopol'd TABURYANSKYY, chairman; Peasants' Party of Ukraine, Serhiy DOVGRAN', chairman; Party of Democratic Rebirth of Ukraine, Volodymyr FILENKO, chairman; Social Democratic Party of Ukraine, Yuriy ZBITNEV, chairman; Socialist Party of Ukraine, Oleksandr MOROZ, chairman; Ukrainian Christian Democratic Party, Vitaliy ZHURAVSKYY, chairman; Ukrainian Conservative Republican Party, Stepan KHMARA, chairman; Ukrainian Labor Party, Valentyn LANDYK, chairman; Ukrainian Party of Justice, Mykhaylo HRECHKO, chairman; Ukrainian Peasants' Democratic Party, Serhiy PLACHINDA, chairman; Ukrainian Republican Party, Mykhaylo HORYN', chairman; Ukrainian National Conservative Party, Viktor RADIONOV, chairman; Ukrainian People's Movement for Restructuring (Rukh), Vyacheslav CHORNOUL, chairman; Ukrainian Communist Party, Petr SYMONENKO
Other political or pressure groups: New Ukraine (Nova Ukrayina); Congress of National Democratic Forces
Member of: BSEC, CBSS (observer), CCC, CE (guest), CEI (participating), CIS, CSCE, EBRD, ECE, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ILO, IMF, INMARSAT, INTELSAT (nonsignatory user), INTERPOL, IOC, ITU, NACC,PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNPROFOR, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO
Diplomatic representation in US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Oleh Hryhorovych BILORUS
chancery: 3350 M Street NW, Suite 200, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: (202) 333-0606
FAX:(202) 333-0817
consulate(s) general: Chicago and New YorkUS diplomatic representation:
chief of mission: Ambassador William MILLER
embassy: 10 Yuria Kotsyubinskovo, 252053 Kiev 53
mailing address: use embassy street address
telephone : [7] (044) 244-7349 or 244-7344
FAX: [7] (044) 244-7350
Economy
CIA Overview: After Russia, the Ukrainian republic was far and away the most important economic component of the former Soviet Union producing more than three times the output of the next-ranking republic. Its fertile black soil generated more than one-fourth of Soviet agricultural output, and its farms provided substantial quantities of meat, milk, grain and vegetables to other republics. Likewise, its diversified heavy industry supplied equipment and raw materials to industrial and mining sites in other regions of the former USSR. In 1992 the Ukrainian Government liberalized most prices and erected a legal framework for privatizing state enterprises while retaining many central economic controls and continuing subsidies to state production enterprises. In November 1992 the new Prime Minister KUCHMA launched a new economic reform program promising more freedom to the agricultural sector, faster privatization of small and medium enterprises, and stricter control over state subsidies. In 1993, however, severe internal political disputes over the scope and pace of economic reform and payment arrears on energy imports have led to further declines in output, and inflation of 50% or more per month by the last quarter. In first quarter 1994, national income and industrial output were less than two-thirds the first quarter 1993 figures, according to official statistics. At the same time an increasing number of people are developing small private businesses and exploiting opportunities in non-official markets. Even so, the magnitude of the problems and the slow pace in building new market-oriented institutions preclude a near-term recovery of output to the 1990 level. A vital economic concern in 1994 will continue to be Russia's decisions on the prices and quantities of oil and gas to be shipped to the Ukraine.
National product: GDP - purchasing power equivalent - $205.4 billion (1993 estimate from the UN International Comparison Program, as extended to 1991 and published in the World Bank's World Development Report 1993; and as extrapolated to 1993 using official Ukrainian statistics, which are very uncertain because of major economic changes since 1990)
National product real growth rate: -16% (1993 est.)
National product per capita: $3,960 (1993 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 45% per month (1993)
Unemployment rate: 0.4% officially registered; large number of unregistered or underemployed workers
Budget:
revenues: $NA
expenditures: $NA, including capital expenditures of $NAExports: $3 billion to countries outside of the FSU (1993)
commodities: coal, electric power, ferrous and nonferrous metals, chemicals, machinery and transport equipment, grain, meat
partners: FSU countries, Germany, China, AustriaImports: $2.2 billion from outside of the FSU countries (1993)
commodities : machinery and parts, transportation equipment, chemicals, textiles
partners: FSU countries, Germany, China, AustriaExternal debt: $NA
Industrial production: growth rate -14% (1993); accounts for 50% of GDP
Electricity:
capacity: 55,882,000 kW
production: 281 billion kWh
consumption per capita: 5,410 kWh (1992)Industries: coal, electric power, ferrous and nonferrous metals, machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, food-processing (especially sugar)
Agriculture: accounts for about 25% of GDP; grain, vegetables, meat, milk, sugar beets
Illicit drugs: illicit cultivator of cannabis and opium poppy; mostly for CIS consumption; limited government eradication program; used as transshipment points for illicit drugs to Western Europe
Economic aid: $350 million economic aid and $350 million to help disassemble the atomic weapons from the US in 1994
Currency: Ukraine withdrew the Russian ruble from circulation on 12 November 1992 and declared the karbovanets (plural karbovantsi) sole legal tender in Ukrainian markets; Ukrainian officials claim this is an interim move toward introducing a new currency - the hryvnya - possibly in mid-1994
Exchange rates: NA
Fiscal year: calendar year
Communications
Railroads: 23,350 km (1,524-mm gauge); 8,600 km electrified
Highways:
total: 273,700 km
paved and gravel: 236,400 km
unpaved: earth 37,300 kmInland waterways: 1,672 km perennially navigable (Pryp'yat' and Dnipro Rivers)
Pipelines: crude oil 2,010 km; petroleum products 1,920 km; natural gas 7,800 km (1992)
Ports: coastal - Berdyans'k, Illichivs'k, Kerch, Kherson, Mariupol', Mykolayiv, Odesa, Sevastopol', Pivdenne; inland - Kiev (Kyyiv)
Merchant marine: 390 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 3,932,009 GRT/5,236,134 DWT, barge carriers 7, bulk cargo 55, cargo 231, chemical tanker 2, container 18, liquefied gas 1, multi-function-large-load-carrier 1, oil tanker 10, passenger 12, passenger cargo 5, railcar carrier 2, refrigerated cargo 5, roll-on/roll-off cargo 33, short-sea passenger 8
Airports:
total: 694
usable: 199
with permanent-surface runways : 111
with runways over 3,659 m: 3
with runways 2,440-3,659 m: 81
with runways 1,060-2,439 m: 78
note: a C-130 can land on a 1,060-m airstripTelecommunications: the telephone system is inadequate both for business and for personal use; about 7,886,000 telephone circuits serve 52,056,000 people (1991); telephone density is 151.4 telephone circuits per 1,000 persons (1991); 3.56 million applications for telephones had not been satisfied as of January 1991; calls to other CIS countries are carried by land line or microwave; other international calls to 167 countries are carried by satellite or by the 150 leased lines through the Moscow gateway switch; an NMT-450 analog cellular telephone network operates in Kiev (Kyyiv) and allows direct dialing of international calls through Kiev's EWSD digital exchange; electronic mail services have been established in Kiev, Odessa, and Lugansk by Sprint; satellite earth stations employ INTELSAT, INMARSAT, and Intersputnik
Defense Forces
Branches: Army, Navy, Air and Air Defense Forces, Republic Security Forces (internal and border troops), National Guard
Manpower availability: males age 15-49 12,191,984; fit for military service 9,591,276; reach military age (18) annually 364,676 (1994 est.)
Defense expenditures: 544,256 million karbovantsi, NA% of GDP (forecast for 1993); note - conversion of the military budget into US dollars using the current exchange rate could produce misleading results.
CIA World Facts (1994)
This page was last up-dated: