| Russia |

|

|
| Russia |

|

|
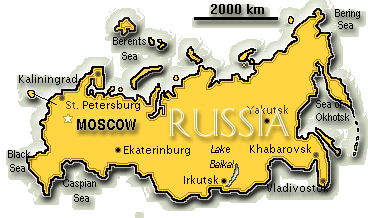
Geography
Location: Northern Asia (that part west of the Urals is sometimes included with Europe), between Europe and the North Pacific Ocean
Area:
total area: 17,075,200 sq km
land area: 16,995,800 sq km
comparative area: slightly more than 1.8 times the size of the US.Land boundaries: total 20,139 km, Azerbaijan 284 km, Belarus 959 km, China (southeast) 3,605 km, China (south) 40 km, Estonia 290 km, Finland 1,313 km, Georgia 723 km, Kazakhstan 6,846 km, North Korea 19 km, Latvia 217 km, Lithuania (Kaliningrad Oblast) 227 km, Mongolia 3,441 km, Norway 167 km, Poland (Kaliningrad Oblast) 432 km, Ukraine 1,576 km.
Coastline: 37,653 km.
Maritime claims:
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to depth of exploitation
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea : 12 nm.International disputes: inherited disputes from former USSR including: sections of the boundary with China; islands of Etorofu, Kunashiri, and Shikotan and the Habomai group occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945, administered by Russia, claimed by Japan; maritime dispute with Norway over portion of the Barents Sea; Russia may dispute current de facto maritime border of midpoint of Caspian Sea from shore; potential dispute with Ukraine over Crimea; has made no territorial claim in Antarctica (but has reserved the right to do so) and does not recognize the claims of any other nation.
Climate: ranges from steppes in the south through humid continental in much of European Russia; subarctic in Siberia to tundra climate in the polar north; winters vary from cool along Black Sea coast to frigid in Siberia; summers vary from warm in the steppes to cool along Arctic coast.
Terrain: broad plain with low hills west of Urals; vast coniferous forest and tundra in Siberia; uplands and mountains along southern border regions.
Natural resources: wide natural resource base including major deposits of oil, natural gas, coal, and many strategic minerals, timber
note: formidable obstacles of climate, terrain, and distance hinder exploitation of natural resources.Land use:
Irrigated land: 56,000 sq km (1992).
arable land: 8%
permanent crops: NA%
meadows and pastures: NA%
forest and woodland: NA%
other: NA%
note: agricultural land accounts for 13% of the total land area
Environment:
current issues: air pollution from heavy industry, emissions of coal-fired electric plants, and transportation in major cities; industrial and agricultural pollution of inland waterways and sea coasts; deforestation; soil erosion; soil contamination from improper application of agricultural chemicals; scattered areas of sometimes intense radioactive contamination. Lake Baikal presents special problems.natural hazards: permafrost over much of Siberia is a major impediment to development.
international agreements: party to Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur, Antarctic Treaty, Environmental Modification, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber, Wetlands; signed, but not ratified Biodiversity, Climate Change, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Antarctic - Environmental Protocol.
Note: largest country in the world in terms of area but unfavorably located in relation to major sea lanes of the world; despite its size, much of the country lacks proper soils and climates (either too cold or too dry) for agriculture.
PeoplePopulation: 149,608,953 (July 1994 est.)
Population growth rate: 0.2% (1994 est.)
Birth rate: 12.67 births/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Death rate: 11.34 deaths/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Net migration rate: 0.7 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 27 deaths/1,000 live births (1994 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population : 68.89 years
male: 63.85 years
female: 74.2 years (1994 est.)Total fertility rate: 1.83 children born/woman (1994 est.)
Nationality:
noun : Russian(s)
adjective: RussianEthnic divisions: Russian 81.5%, Tatar 3.8%, Ukrainian 3%, Chuvash 1.2%, Bashkir 0.9%, Byelorussian 0.8%, Moldavian 0.7%, other 8.1%
Religions: Russian Orthodox, Muslim, other.
Languages: Russian, other European, Caucasian, and Asian languages
Literacy: age 9-49 can read and write (1970)
total population : 100%
male: 100%
female: 100%Labor force: 75 million (1993 est.)
by occupation : production and economic services 83.9%, government 16.1%
GovernmentNames:
conventional long form: Russian Federation
conventional short form: Russia
local long form : Rossiyskaya Federatsiya
local short form: Rossiya
former: Russian Soviet Federative Socialist RepublicDigraph: RS
Type: federation
Capital: Moscow
Administrative divisions: 21 autonomous republics (avtomnykh respublik, singular - avtomnaya respublika); Adygea (Maykop), Bashkortostan (Ufa), Buryatia (Ulan-Ude), Chechenia (Groznyy), Chuvashia (Cheboksary), Dagestan (Makhachkala), Gorno-Altay (Gorno-Altaysk), Ingushetia (Nazran'), Kabardino-Balkaria (Nal'chik), Kalmykia (Elista), Karachay-Cherkessia (Cherkessk), Karelia (Petrozavodsk), Khakassia (Abakan), Komi (Syktyvkar), Mari El (Yoshkar-Ola), Mordovia (Saransk), North Ossetia (Vladikavkaz), Tatarstan (Kazan'), Tuva (Kyzyl), Udmurtia (Izhevsk), Yakutia (Yakutsk); 49 oblasts (oblastey, singular - oblast'); Amur (Blagoveshchensk), Arkhangel'sk, Astrakhan, Belgorod, Bryansk, Chelyabinsk, Chita, Irkutsk, Ivanovo, Kaliningrad, Kaluga, Kamchatka (Petropavlovsk-Kamchatskiy), Kemerovo, Kirov, Kostroma, Kurgan, Kursk, Lipetsk, Magadan, Moscow, Murmansk, Nizhniy Novgorod, Novgorod, Novosibirsk, Omsk, Orel, Orenburg, Penza, Perm, Pskov, Rostov, Ryazan, Sakhalin (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk), Samara, Saratov, Smolensk, St. Petersburg, Sverdlovsk (Yekaterinburg), Tambov, Tomsk, Tula, Tver', Tyumen', Ul'yanovsk, Vladimir, Volgograd, Vologda, Voronezh, Yaroslavl; 6 krays (krayev, singular - kray); Altay (Barnaul), Khabarovsk, Krasnodar, Krasnoyarsk, Primorskiy (Vladivostok), Stavropol'.
note: the autonomous republics of Chechenia and Ingushetia were formerly the automous republic of Checheno-Ingushetia (the boundary between Chechenia and Ingushetia has yet to be determined); the cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg are federal cities; an administrative division has the same name as its administrative center (exceptions have the administrative center name following in parentheses).
Independence: 24 August 1991 (from Soviet Union)
National holiday: Independence Day, June 12 (1990)
Constitution: adopted 12 December 1993
Legal system: based on civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: President Boris Nikolayevich YEL'TSIN (since 12 June 1991) election last held 12 June 1991 (next to be held 1996); results - percent of vote by party NA%; note - no vice president; if the president dies in office, cannot exercise his powers because of ill health, is impeached, or resigns, the premier succeeds him; the premier serves as acting president until a new presidential election, which must be held within three months.
head of government: Premier and Chairman of the Council of Ministers Evgenii Primakov (since 1998); First Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers Oleg SOSKOVETS (since 30 April 1993)
Security Council: (originally established as a presidential advisory body in June 1991, but restructured in March 1992 with responsibility for managing individual and state security).Presidential Administration: (drafts presidential edicts and provides staff and policy support to the entire executive branch).
cabinet: Council of Ministers; appointed by the president
Group of Assistants: (schedules president's appointments, processes presidential edicts and other official documents, and houses the president's press service and primary speechwriters)
Council of Heads of Republics: (includes the leaders of the 21 ethnic-based Republics)
Council of Heads of Administrations: (includes the leaders of the 68 autonomous territories and regions, and the mayors of Moscow and St. Petersburg)
Presidential Council: (prepares policy papers for the president)Legislative branch: bicameral Federal Assembly
Federation Council: elections last held 12 December 1993 (next to be held NA); note - two members elected from each of Russia's 89 territorial units for a total of 176 deputies; 2 seats unfilled as of 15 May 1994 (Chechenia did not participate in the election); Speaker Vladimir SHUMEYKO (Russia's Choice)
State Duma: elections last held 12 December 1993 (next to be held NA December 1995); results - percent of vote by party NA; seats - (450 total) Russia's Choice 78, New Regional Policy 66, Liberal Democrats 63, Agrarian Party 55, Communist Party of the Russian Federation 45, Unity and Accord 30, Yavlinskiy Bloc 27, Women of Russia 23, Democratic Party of Russia 15, Russia's Path 12, other parties 23, affiliation unknown 12, unfilled (as of 13 March 1994; Chechnya did not participate in the election) 1; Speaker Ivan RYBKIN (Agrarian Party)Judicial branch: Constitutional Court, Supreme Court (highest court for criminal, civil, and administrative cases), Superior Court of Arbitration (highest court that resolves economic disputes)
Political parties and leaders:
pro-market democrats : Party of Russian Unity and Accord, Sergey SHAKHRAY; Russia's Choice electoral association, Yegor GAYDAR; Russian Movement for Democratic Reforms electoral association, Anatoliy SOBCHAK; Yavlinskiy-Boldyrev-Lukin Bloc electoral association, Grigoriy YAVLINSKIY
centrists/special interest parties: Civic Union for Stability, Justice, and Progress, Arkadiy VOL'SKIY; Constructive-Ecological Movement of Russia, Anatoliy PANFILOV; Democratic Party of Russia, Nikolay TRAVKIN; Dignity and Charity Federal Political Movement, Konstantin FROLOV; Russia's Future-New Names electoral association, Vyacheslav LASHCHEVSKIY; Women of Russia Party, Alevtina FEDULOVA.
anti-market and/or ultranationalist parties : Agrarian Party, Mikhail LAPSHIN; Communist Party of the Russian Federation, Gennadiy ZYUGANOV; Liberal Democratic Party of Russia, Vladimir ZHIRINOVSKIY
note: more than 20 political parties and associations tried to gather enough signatures to run slates of candidates in the 12 December 1993 legislative elections, but only 13 succeededOther political or pressure groups: NA
Member of: BSEC, CBSS, CCC, CE (guest), CERN (observer), CIS, CSCE, EBRD, ECE, ESCAP, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IFC, ILO, IMF, IMO, INMARSAT, INTELSAT, INTERPOL, IOC, IOM (observer), ISO, ITU, LORCS, MINURSO, NACC, NSG, OAS (observer), PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIKOM, UNOMOZ, UNPROFOR, UN Security Council, UNTAC, UN Trusteeship Council, UNTSO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in US:
chief of mission : Ambassador Vladimir Petrovich LUKIN
chancery: 1125 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: (202) 628-7551 and 8548
consulate(s) general: New York, San Francisco, and Seattle
consulate(s): WashingtonUS diplomatic representation:
chief of mission: Ambassador Thomas R. PICKERING
embassy: Novinskiy Bul'var 19/23, Moscow
mailing address: APO AE 09721
telephone: [7] (095) 252-2451 through 2459
FAX: [7] (095)-4261/4270
consulate(s): St. Petersburg, Vladivostok
EconomyThe Russian Economy Resource Center
CIA Overview: Russia, a vast country with a wealth of natural resources, a well-educated population,and a diverse industrial base, continues to experience severe difficulties in moving from its old centrally planned economy to a modern market economy. President YEL'TSIN's government has made some progress toward a market economy by freeing most prices, slashing defense spending, unifying foreign exchange rates, and launching an ambitious privatization program. Yet much of the old order persists and YEL'TSIN faces formidable opposition to further measures such as the reduction of subsidies to old-line industries. Output continues to fall although the mix is gradually becoming more responsive to Russia's needs. According to Russian official data, GDP declined by 12% in 1993 compared with 19% in 1992. Industrial output in 1993 fell 16% with all major sectors taking a hit. Agricultural production, meanwhile, was down 6%. The grain harvest totalled 99 million tons - some 8 million tons less than in 1992. Unemployment climbed in 1993 but remained low by Western standards. The official number of unemployed rose from 578,000 at the beginning of 1993 to about 1 million - or roughly 1.4% of the work force - by yearend. According to the Russian labor minister, the actual number of unemployed probably was closer to 4 million. Government fears of large-scale unemployment continued to hamper industrial restructuring efforts. According to official statistics, average real wages remained flat. Nonetheless, a substantial portion of the population, particularly the elderly and people in remote areas, finds its well-being steadily shrinking. The disparity in incomes between the rich and poor continued to rise in 1993, primarily reflecting the high earnings of enterprise managers and persons employed in the emerging private sector. The government tried to narrow the income gap by raising the wages of budget-funded workers - mainly teachers and health care specialists. Official data may overstate hardships, because many Russians supplement their income by moonlighting or by bartering goods and services, activities that often go unreported. Russia made good progress on privatization in 1993 despite active opposition from key cabinet members,hard-line legislators, and antireform regional leaders. By yearend, for example,roughly 35% of Russia's medium and large state enterprises had been auctioned,while the number of private farms in Russia increased by 86,000, reaching a total of 170,000. As a result, about 6% of agricultural land now has been privatized. Financial stabilization continued to remain a challenge for the government. Moscow tightened financial policies in early 1993 - including postponing planned budget spending - and succeeded in reducing monthly inflation from 27% in January to 20% in May and June. In the summer, however, the government relaxed austerity measures in the face of mounting pressure from industry and agriculture, sparking a new round of inflation; the monthly inflation rate jumped to 25% in August. In response, Moscow announced a package of measures designed to curb government spending and inflation. It included eliminating bread subsidies, delaying payment obligations, raising interest rates, and phasing out concessionary Central Bank credits to enterprises and regions. The measures met with some success; the monthly inflation rate declined to 13% in December. According to official statistics, Russia's 1993 trade with nations outside the former Soviet Union produced a $16 billion surplus, up from $6 billion in 1992. Moscow arrested the steep drop in exports that it had been suffering as a result of ruptured ties with former trading partners,output declines, and erratic efforts to move to world prices. Foreign sales - comprised largely of oil, natural gas, and other raw materials - grew slightly. Imports were down by 15% or so as a result of new import taxes and Moscow's reluctance to increase its debt burden by purchasing grain and other goods with foreign credits. Russian trade with other former Soviet republics continued to decline and yielded a surplus of some $5 billion. At the same time, Russia paid only a fraction of the roughly $20 billion in debt coming due in 1993,and by mid-year, Russia's foreign debt had amounted to $81.5 billion. While Moscow reached agreement to restructure debts with Paris Club official creditors in April 1993, Moscow's refusal to waive its right to sovereign immunity kept Russia and its bank creditors from agreeing to restructure Moscow's commercial loans. Capital flight continued to be a serious problem in 1993, with billions of dollars in assets owned by Russians being parked abroad at yearend. Russia's capital stock continues to deteriorate because of insufficient maintenance and new construction. The capital stock on average is twice the age of capital stock in the West. Many years will pass before Russia can take full advantage of its natural resources and its human assets.
National product: GDP - purchasing power equivalent - $775.4 billion (1993 estimate from the UN International Comparison Program, as extended to 1991 and published in the World Bank's World Development Report 1993; and as extrapolated to 1993 using official Russian statistics, which are very uncertain because of major economic changes since 1990)
National product real growth rate: -12% (1993 est.)
National product per capita: $5,190 (1993 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 21% per month (average 1993); 13% per month (December 1993)
Unemployment rate: 1.4% (1 January 1994; official data)
Budget:
revenues: $NA
expenditures: $NA, including capital expenditures of $NAExports: $43 billion (f.o.b., 1993)
commodities : petroleum and petroleum products, natural gas, wood and wood products,metals, chemicals, and a wide variety of civilian and military manufactures
partners: Europe, North America, Japan, Third World countries, CubaImports: $27 billion (f.o.b., 1993)
commodities: machinery and equipment, chemicals, consumer goods, grain, meat, sugar, semifinished metal products
partners: Europe, North America, Japan, Third World countries, CubaExternal debt: $81.5 billion (mid-year 1993 est.)
Industrial production: growth rate -16% (1993 est.)
Electricity:
capacity: 213,000,000 KW
production: 956 billion kWh
consumption per capita: 6,782 kWh (1 January 1992)Industries: complete range of mining and extractive industries producing coal, oil, gas, chemicals, and metals; all forms of machine building from rolling mills to high-performance aircraft and space vehicles; ship- building; road and rail transportation equipment; communications equipment; agricultural machinery, tractors, and construction equipment; electric power generating and transmitting equipment; medical and scientific instruments; consumer durables
Agriculture: grain, sugar beet, sunflower seeds, meat, milk, vegetables, fruits; because of its northern location does not grow citrus, cotton, tea, and other warm climate products
Illicit drugs: illicit cultivator of cannabis and opium poppy; mostly for domestic consumption; government has active eradication program; used as transshipment point for Asian and Latin American illicit drugs to Western Europe and Latin America
Economic aid:
recipient: US commitments, including Ex-Im (1990-93), $13 billion; other countries, ODA and OOF bilateral commitments (1988-93), $115 billionCurrency: 1 ruble (R) = 100 kopeks
Exchange rates: rubles per US$1 - 1,247 (27 December 1993), 415 (24 December 1992); nominal exchange rate still deteriorating but real exchange rate strengthening
Fiscal year: calendar year
CommunicationsRailroads: 158,100 km all 1.520-meter broad gauge; 86,800 km in common carrier service, of which 48,900 km are diesel traction and 37,900 km are electric traction; 71,300 km serves specific industry and is not available for common carrier use (30 June 1993)
Highways:
total: 893,000 km
paved and gravel: 677,000 km
unpaved : 216,000 kmInland waterways: total navigable routes in general use 100,000 km; routes with navigation guides serving the Russian River Fleet 95,900 km; of which routes with night navigational aids 60,400 km; man-made navigable routes 16,900 km (30 June 1993)
Pipelines: crude oil 48,000 km; petroleum products 15,000 km; natural gas 140,000 km (30 June 1993)
Ports: coastal - St. Petersburg, Kaliningrad, Murmansk, Petropavlovsk, Arkhangel'sk, Novorossiysk, Vladivostok, Nakhodka, Kholmsk, Korsakov, Magadan, Tiksi, Tuapse, Vanino, Vostochnyy, Vyborg; inland - Astrakhan', Nizhniy Novgorod, Kazan', Khabarovsk, Krasnoyarsk, Samara, Moscow, Rostov, Volgograd
Merchant marine: 867 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 8,084,988 GRT/11,124,929 DWT, barge carrier 2, bulk cargo 26, cargo 454, chemical tanker 9, combination bulk 28, combination ore/oil 16, container 82, multi-function large load carrier 3, oil tanker 125, passenger 6, passenger cargo 5, refrigerated cargo 17, roll-on/roll-off cargo 74, short-sea passenger 18, specialized tanker 2
Airports:
total : 2,550
usable: 964
with permanent-surface runways : 565
with runways over 3,659 m: 19
with runways 2,440-3,659 m : 275
with runways 1,220-2,439 m: 426Telecommunications: Russia is enlisting foreign help, by means of joint ventures, to speed up the modernization of its telecommunications system; NMT-450 analog cellular telephone networks are operational and growing in Moscow and St. Petersburg; expanded access to international E-mail service available via Sprint network; intercity fiberoptic cable installation remains limited; the inadequacy of Russian telecommunications is a severe handicap to the economy, especially with respect to international connections; total installed telephones 24,400,000, of which in urban areas 20,900,000 and in rural areas 3,500,000; of these, total installed in homes 15,400,000; total pay phones for long distant calls 34,100; telephone density is about 164 telephones per 1,000 persons (in 1992, only 661,000 new telephones were installed compared with 855,000 in 1991 and in 1992 the number of unsatisfied applications for telephones reached 11,000,000); international traffic is handled by an inadequate system of satellites, land lines, microwave radio relay and outdated submarine cables; this traffic passes through the international gateway switch in Moscow which carries most of the international traffic for the other countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States; a new Russian Raduga satellite will link Moscow and St. Petersburg with Rome from whence calls will be relayed to destinations in Europe and overseas; satellite ground stations - INTELSAT, Intersputnik, Eutelsat (Moscow),INMARSAT, Orbita; broadcast stations - 1,050 AM/FM/SW (reach 98.6% of population), 7,183 TV; receiving sets - 54,200,000 TVs, 48,800,000 radio receivers, 74,300,000 radio receivers with multiple speaker systems for program diffusion
Defense ForcesBranches: Ground Forces, Navy,Air Forces, Air Defense Forces, Strategic Rocket Forces, Command and General Support, Security Forces
Manpower availability: males age 15-49 37,706,825; fit for military service 29,623,429; reach military age (18) annually 1,098,307 (1994 est.)
Defense expenditures: $NA, NA% of GDP
CIA World Facts (1994)
This page was last up-dated:




