Lithuania

Geography
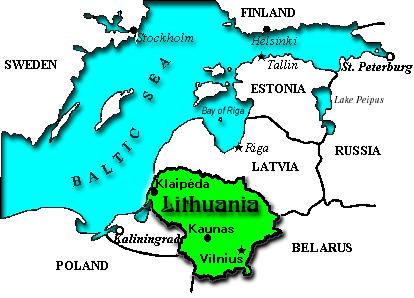
Location: Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, between Sweden and RussiaArea:
total area: 65,200 sq km
land area: 65,200 sq km
comparative area: slightly larger than West VirginiaLand boundaries: total 1,273 km, Belarus 502 km, Latvia 453 km, Poland 91 km, Russia (Kaliningrad) 227 km
Coastline: 108 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea: 12 nmInternational disputes: dispute with Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast) over the position of the Nemunas (Nemen) River border presently located on the Lithuanian bank and not in midriver as by international standards
Climate: maritime; wet, moderate winters and summers
Terrain: lowland, many scattered small lakes, fertile soil
Natural resources: peat
Land use:
arable land: 49.1%
permanent crops: 0%
meadows and pastures: 22.2%
forest and woodland: 16.3%
other: 12.4%Irrigated land: 430 sq km (1990)
Environment:
current issues: contamination of soil and groundwater with petroleum products and chemicals at military bases
natural hazards: NA
international agreements: party to - Ship Pollution; signed, but not ratified - Biodiversity, Climate Change
People
Population: 3,848,389 (July 1994 est.)
Population growth rate: 0.74% (1994 est.)
Birth rate: 14.71 births/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Death rate: 10.95 deaths/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Net migration rate: 3.62 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 16.7 deaths/1,000 live births (1994 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population : 71.24 years
male: 66.53 years
female: 76.19 years (1994 est.)Total fertility rate: 2.01 children born/woman (1994 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Lithuanian(s)
adjective: LithuanianEthnic divisions: Lithuanian 80.1%, Russian 8.6%, Polish 7.7%, Byelorussian 1.5%, other 2.1%
Religions: Roman Catholic, Lutheran, other
Languages: Lithuanian (official), Polish, Russian
Literacy: age 9-49 can read and write (1989)
total population: 98%
male: 99%
female: 98%Labor force: 1.836 million
by occupation: industry and construction 42%, agriculture and forestry 18%, other 40% (1990)
Government
Names:
conventional long form: Republic of Lithuania
conventional short form: Lithuania
local long form: Lietuvos Respublika
local short form: Lietuva
former: Lithuanian Soviet Socialist RepublicDigraph: LH
Type: republic
Capital: Vilnius
Administrative divisions: 44 regions (rajonai, singular - rajonas) and 11 municipalities*: Akmenes Rajonas, Alytaus Rajonas, Alytus*, Anyksciu Rajonas, Birsionas*, Birzu Rajonas, Druskininkai*, Ignalinos Rajonas, Jonavos Rajonas, Joniskio Rajonas, Jurbarko Rajonas, Kaisiadoriu Rajonas, Marijampoles Rajonas, Kaunas*, Kauno Rajonas, Kedainiu Rajonas, Kelmes Rajonas, Klaipeda*, Klaipedos Rajonas, Kretingos Ragonas, Kupiskio Rajonas, Lazdiju Rajonas, Marijampole*, Mazeikiu Ragonas, Moletu Rajonas, Neringa* Pakruojo Rajonas, Palanga*, Panevezio Rajonas, Panevezys*, Pasvalio Rajonas, Plunges Rajonas, Prienu Rajonas, Radviliskio Rajonas, Raseiniu Rajonas, Rokiskio Rajonas, Sakiu Rajonas, Salcininky Rajonas, Siauliai*, Siauliu Rajonas, Silales Rajonas, Siltues Rajonas, Sirvinty Rajonas, Skuodo Rajonas, Svencioniu Rajonas, Taurages Rajonas, Telsiu Rajonas, Traky Rajonas, Ukmerges Rajonas, Utenos Rajonas, Varenos Rajonas, Vilkaviskio Rajonas, Vilniaus Rajonas, Vilnius*, Zarasu Rajonas
Independence: 6 September 1991 (from Soviet Union)
National holiday: Independence Day, 16 February (1918)
Constitution: adopted 25 October 1992
Legal system: based on civil law system; no judicial review of legislative acts
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: President Algirdas Mykolas BRAZAUSKAS (since 25 November 1992; elected acting president by Parliament 25 November 1992 and elected by direct vote 15 February 1993); election last held 14 February 1993 (next to be held NA 1997); results - Algirdas BRAZAUSKAS was elected; note - on 25 November 1992 BRAZAUSKAS was elected chairman of Parliament and, as such, acting president of the Republic; he was confirmed in office by direct balloting 15 February 1993
head of government : Premier Adolfas SLEZEVICIUS (since 10 March 1993)
cabinet: Council of Ministers; appointed by the president on the nomination of the prime ministerLegislative branch: unicameral
Seimas (parliament) : elections last held 26 October and 25 November 1992 (next to be held NA); results - LDDP 51%; seats - (141 total) LDDP 73, Conservative Party 30, LKDP 17, LTS 8, Farmers' Union 4, LLS 4, Center Union 2, others 3Judicial branch: Supreme Court, Court of Appeals
Political parties and leaders: Christian Democratic Party (LKDP), Povilas KATILIUS, chairman; Democratic Labor Party of Lithuania (LDDP), Adolfas SLEZEVICIUS, chairman; Lithuanian Nationalist Union (LTS), Rimantas SMETONA, chairman; Lithuanian Social Democratic Party (LSDP), Aloyzas SAKALAS, chairman; Farmers' Union, Jonas CIULEVICIUS, chairman; Center Union, Romualdas OZOLAS, chairman; Conservative Party, Vytautas LANDSBERGIS, chairman; Lithuanian Polish Union (LLS), Rytardas MACIKIANEC, chairman
Other political or pressure groups: Homeland Union; Lithuanian Future Forum; Farmers Union
Member of: BIS, CBSS, CCC, CE, CSCE, EBRD, ECE, FAO, IBRD, ICAO, ILO, IMF, INTELSAT (nonsignatory user), INTERPOL, IOC, ISO (correspondent), ITU, LORCS, NACC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO
Diplomatic representation in US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Alfonsas EIDINTAS
chancery: 2622 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone: (202) 234-5860, 2639
FAX: (202) 328-0466
consulate(s) general: New YorkUS diplomatic representation:
chief of mission: Ambassador Darryl N. JOHNSON
embassy : Akmenu 6, Vilnius 232600
mailing address: APO AE 09723
telephone: 370-2-223-031
FAX: 370-2-222-779
Economy
CIA Overview: Since independence in September 1991, Lithuania has made steady progress in developing a market economy. Over 40% of state property has been privatized and trade is diversifying with a gradual shift away from the former Soviet Union to Western markets. Nevertheless, the process has been painful with industrial output in 1993 less than half the 1991 level. Inflation, while lower than in most ex-Soviet states, has exceeded rates in the other Baltic states. Full monetary stability and economic recovery are likely to be impeded by periodic government backtracking on key elements of its reform and stabilization program as it seeks to ease the economic pain of restructuring. Recovery will build on Lithuanian's strategic location with its ice-free port at Klaipeda and its rail and highway hub in Vilnius connecting it with Eastern Europe, Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine, and on its agriculture potential, highly skilled labor force, and diversified industrial sector. Lacking important natural resources, it will remain dependent on imports of fuels and raw materials.
National product: GDP - purchasing power equivalent - $12.4 billion (1993 estimate from the UN International Comparison Program, as extended to 1991 and published in the World Bank's World Development Report 1993; and as extrapolated to 1993 using official Lithuanian statistics, which are very uncertain because of major economic changes since 1990)
National product real growth rate: -10% (1993 est.)
National product per capita: $3,240 (1993 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 188% (1993)
Unemployment rate: 1.8% (July 1993)
Budget:
revenues: $258.5 million
expenditures: $270.2 million, including capital expenditures of $NA (1992 est.)Exports: $NA
commodities: electronics 18%, petroleum products 5%, food 10%, chemicals 6% (1989)
partners: Russia 40%, Ukraine 16%, other FSU countries 32%, West 12%Imports: $NA
commodities: oil 24%, machinery 14%, chemicals 8%, grain NA% (1989)
partners: Russia 62%, Belarus 18%, other FSU countries 10%, West 10%External debt: $NA
Industrial production: growth rate -52% (1992)
Electricity:
capacity: 5,925,000 kW
production: 25 billion kWh
consumption per capita: 6,600 kWh (1992)Industries: employs 42% of the labor force; accounts for 23% of GOP shares in the total production of the former USSR are: metal-cutting machine tools 6.6%; electric motors 4.6%; television sets 6.2%; refrigerators and freezers 5.4%; other branches: petroleum refining, shipbuilding (small ships), furniture making, textiles, food processing, fertilizers, agricultural machinery, optical equipment, electronic components, computers, and amber
Agriculture: employs around 18% of labor force; accounts for 25% of GDP; sugar, grain, potatoes, sugar beets, vegetables, meat, milk, dairy products, eggs, fish; most developed are the livestock and dairy branches, which depend on imported grain; net exporter of meat, milk, and eggs
Illicit drugs: transshipment point for illicit drugs from Central and Southwest Asia and Latin America to Western Europe; limited producer of illicit opium; mostly for domestic consumption
Economic aid:
recipient: US commitments, including Ex-Im (1992), $10 million; Western (non-US) countries, ODA and OOF bilateral commitments (1970-86), $NA million; Communist countries (1971-86), $NA millionCurrency: introduced the convertible litas in June 1993
Exchange rates: litai per US$1 - 4 (fixed rate 1 May 1994); 3.9 (late January 1994)
Fiscal year: calendar year
Communications
Railroads: 2,000 km (1,524-mm gauge); 120 km electrified
Highways:
total: 44,200 km
paved: 35,500 km
unpaved: earth 8,700 km (1990)Inland waterways: 600 km perennially navigable
Pipelines: crude oil, 105 km; natural gas 760 km (1992)
Ports: coastal - Klaipeda; inland - Kaunas
Merchant marine: 44 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 276,265 GRT/323,505 DWT, cargo 29, combination bulk 11, railcar carrier 3, roll-on/roll-off cargo 1
Airports:
total: 96
usable: 18
with permanent-surface runways: 12
with runways over 3,659 m: 0
with runways 2,440-3,659 m: 5
with runways 1,060-2,439 m: 11
note: a C-130 can land on a 1,060-m airstripTelecommunications: Lithuania ranks among the most modern of the former Soviet republics in respect to its telecommunications system; telephone subscriber circuits 900,000; subscriber density 240 per 1,000 persons; land lines or microwave to former USSR republics; international connections no longer depend on the Moscow gateway switch, but are established by satellite through Oslo from Vilnius and through Copenhagen from Kaunas; 2 satellite earth stations - 1 EUTELSAT and 1 INTELSAT; an NMT-450 analog cellular network operates in Vilnius and other cities and is linked internationally through Copenhagen by EUTELSAT; international electronic mail is available; broadcast stations - 13 AM, 26 FM, 1 SW, 1 LW, 3 TV
Defense Forces
Branches: Ground Forces, Navy, Air Force, Security Forces (internal and border troops), National Guard (Skat)
Manpower availability: males age 15-49: 941,273; fit: for military service 744,867; reach military age (18) annually: 27,375 (1994 est.)
Defense expenditures: exchange rate conversion - $NA, 5.5% of GDP (1993 est.)
CIA World Facts (1994)
This page was last up-dated:
