Latvia
Geography
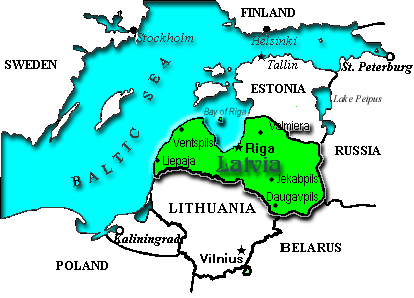
Location: Eastern Europe, bordering on the Baltic Sea, between Sweden and RussiaArea:
total area : 64,100 sq km
land area: 64,100 sq km
comparative area : slightly larger than West VirginiaLand boundaries: total 1,078 km, Belarus 141 km, Estonia 267 km, Lithuania 453 km, Russia 217 km
Coastline: 531 km
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: 12 nmInternational disputes: the Abrene section of border ceded by the Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic to Russia in 1944
Climate: maritime; wet, moderate winters
Terrain: low plain
Natural resources: minimal; amber, peat, limestone, dolomite
Land use:
arable land: 27%
permanent crops: 0%
meadows and pastures: 13%
forest and woodland : 39%
other: 21%Irrigated land: 160 sq km (1990)
Environment:
current issues: air and water pollution because of a lack of waste conversion equipment; Gulf of Riga and Daugava River heavily polluted; contamination of soil and groundwater with chemicals and petroleum products at military bases
natural hazards : NA
international agreements: party to - Hazardous Wastes, Ship Pollution; signed, but not ratified - Biodiversity, Climate Change
People
Population: 2,749,211 (July 1994 est.)
Population growth rate: 0.5% (1994 est.)
Birth rate: 13.84 births/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Death rate: 12.61 deaths/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Net migration rate: 3.74 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 21.5 deaths/1,000 live births (1994 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 69.44 years
male: 64.37 years
female: 74.75 years (1994 est.)Total fertility rate: 1.98 children born/woman (1994 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Latvian(s)
adjective: LatvianEthnic divisions: Latvian 51.8%, Russian 33.8%, Byelorussian 4.5%, Ukrainian 3.4%, Polish 2.3%, other 4.2%
Religions: Lutheran, Roman Catholic, Russian Orthodox
Languages: Lettish (official), Lithuanian, Russian, other
Literacy: age 9-49 can read and write (1970)
total population: 100%
male: 100%
female: 100%Labor force: 1.407 million
by occupation: industry and construction 41%, agriculture and forestry 16%, other 43% (1990)
Government
Names:
conventional long form: Republic of Latvia
conventional short form: Latvia
local long form: Latvijas Republika
local short form: Latvija
former: Latvian Soviet Socialist RepublicDigraph: LG
Type: republic
Capital: Riga
Administrative divisions: 26 counties (singular - rajons) and 7 municipalities*: Aizkraukles Rajons, Aluksnes Rajons, Balvu Rajons, Bauskas Rajons, Cesu Rajons, Daugavpils*, Daugavpils Rajons, Dobeles Rajons, Gulbenes Rajons, Jekabpils Rajons, Jelgava*, Jelgavas Rajons, Jurmala*, Kraslavas Rajons, Kuldigas Rajons, Leipaja*, Liepajas Rajons, Limbazu Rajons, Ludzas Rajons, Madonas Rajons, Ogres Rajons, Preiju Rajons, Rezekne*, Rezeknes Rajons, Riga*, Rigas Rajons, Saldus Rajons, Talsu Rajons, Tukuma Rajons, Valkas Rajons, Valmieras Rajons, Ventspils*, Ventspils Rajons
Independence: 6 September 1991 (from Soviet Union)
National holiday: Independence Day, 18 November (1918)
Constitution: newly elected Parliament in 1993 restored the 1933 constitution
Legal system: based on civil law system
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: President Guntis ULMANIS (since 7 July 1993); Saeima elected President ULMANIS in the third round of balloting on 7 July 1993
head of government: Prime Minister Valdis BIRKAVS (since 20 July 1993)
cabinet: Council of Ministers; appointed by the Supreme CouncilLegislative branch: unicameral
Parliament (Saeima) : elections last held 5-6 June 1993 (next to be held NA June 1996); results - percent of vote by party NA; seats - (100 total) LC 36, LNNK 15, Concord for Latvia 13, LZS 12, Equal Rights 7, LKDS 6, TUB 6, DCP 5Judicial branch: Supreme Court
Political parties and leaders: Latvian Way Union (LC), Valdis BIRKAVS; Latvian Farmers Union (LZS), Alvars BERKIS; Latvian National Independence Movement (LNNK), Andrejs KRASTINS, Aristids LAMBERGS, cochairmen; Concord for Latvia, Janis JURKANS; Equal Rights, Sergejs DIMANIS; Christian Democrat Union (LKDS), Peteris CIMDINS, Andris SAULITIS, Janis RUSKO; Fatherland and Freedom (TUB), Maris GRINBLATS, Roberts MILBERGS, Oigerts DZENTIS; Democratic Center (DCP), Ints CALITIS; Popular Front of Latvia (LTF), Uldis AUGSTKALNS
Member of: BIS, CBSS, CCC, CE (guest), CSCE, EBRD, ECE, FAO, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IFC, ILO, IMF, IMO, INTELSAT (nonsignatory user), INTERPOL, IOC, IOM (observer), ITU, LORCS, NACC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO
Diplomatic representation in US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Ojars Eriks KALNINS
chancery: 4325 17th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
telephone : (202) 726-8213 and 8214US diplomatic representation:
chief of mission: Ambassador Ints M, SILINS
embassy : Raina Boulevard 7, Riga 226050
mailing address: use embassy street address
telephone: 46-9-882-0046
FAX: 46-9-882-0047
Economy
CEEBIC Economic UpdatesCIA Overview: Latvia is rapidly becoming a dynamic market economy, rivaled only by Estonia among the former Soviet states in the speed of its transformation. The transition has been painful with GDP falling over 45% in 1992-93, according to official statistics, and industrial production experiencing even steeper declines. Nevertheless, the government's tough monetary policies and reform program, which foster the development of the private sector and market mechanisms, have kept inflation low, created a dynamic private sector - much of which is not captured in official statistics - and expanded trade ties with the West. Much of agriculture is already privatized and the government plans to step up the pace of privatization of state enterprises. The economy is now poised for recovery and will benefit from the country's strategic location on the Baltic Sea, its well-educated population, and its diverse - albeit largely obsolete - industrial structure.
National product: GDP - purchasing power equivalent - $13.2 billion (1993 estimate from the UN International Comparison Program, as extended to 1991 and published in the World Bank's World Development Report 1993; and as extrapolated to 1993 using official Latvian statistics, which are very uncertain because of major economic changes since 1990)
National product real growth rate: -5% (1993 est.)
National product per capita: $4,810 (1993 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 2% per month (1993 average)
Unemployment rate: 5.6% (December 1993)
Budget:
revenues: $NA
expenditures: $NA, including capital expenditures of $NAExports: $429 million from non-FSU countries (f.o.b., 1992)
commodities: oil products, timber, ferrous metals, dairy products, furniture, textiles
partners: Russia, other CIS countries, Western EuropeImports: $NA
commodities: fuels, cars, ferrous metals, chemicals
partners: Russia, other CIS countries, Western EuropeExternal debt: $NA
Industrial production: growth rate -38% (1992 est.)
Electricity:
capacity: 2,140,000 kW
production: 5.8 billion kWh
consumption per capita: 2,125 kWh (1992)Industries: employs 41% of labor force; highly diversified; dependent on imports for energy, raw materials, and intermediate products; produces buses, vans, street and railroad cars, synthetic fibers, agricultural machinery, fertilizers, washing machines, radios, electronics, pharmaceuticals, processed foods, textiles
Agriculture: employs 16% of labor force; principally dairy farming and livestock feeding; products - meat, milk, eggs, grain, sugar beets, potatoes, vegetables; fishing and fish packing
Illicit drugs: transshipment point for illicit drugs from Central and Southwest Asia and Latin America to Western Europe; limited producer of illicit opium; mostly for domestic consumption; also produces illicit amphetamines for export
Economic aid: $NA
Currency: 1 lat = 100 cents; introduced NA March 1993
Exchange rates: lats per US$1 - 0.5917 (January 1994), 1.32 (March 1993)
Fiscal year: calendar year
Communications
Railroads: 2,400 km (1,524-mm gauge); 270 km electrified
Highways:
total: 59,500 km
paved and graveled: 33,000 km
unpaved: earth 26,500 km (1990)Inland waterways: 300 km perennially navigable
Pipelines: crude oil 750 km; refined products 780 km; natural gas 560 km (1992)
Ports: coastal - Riga, Ventspils, Liepaja; inland - Daugavpils
Merchant marine: 93 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 850,840 GRT/1,107,403 DWT, cargo 15, container 2, oil tanker 41, refrigerated cargo 27, roll-on/roll-off cargo 8
Airports:
total: 50
usable: 15
with permanent-surface runways: 11
with runways over 3,659 m : 0
with runways 2,440-3,659 m: 7
with runways 1,060-2,439 m : 7
note: a C-130 can land on a 1,060-m airstripTelecommunications: Latvia is better provided with telephone service than most of the other former Soviet republics; subscriber circuits 660,000; subscriber density 240 per 1,000 persons (1993); an NMT-450 analog cellular telephone network covers 75% of Latvia's population; international traffic carried by leased connection to the Moscow international gateway switch and through the new Ericsson AXE local/transit digital telephone exchange in Riga and through the Finnish cellular net; electronic mail capability by Sprint data network; broadcasting services NA
Defense Forces
Branches: Ground Forces, Navy, Air Force, Security Forces (internal and border troops), Border Guard, Home Guard (Zemessardze)
Manpower availability: males age 15-49: 652,444; fit for military service: 514,055; reach military age (18) annually: 18,803 (1994 est.)
Defense expenditures: 176 million rubles, 3%-5% of GDP; note - conversion of the military budget into US dollars using the prevailing exchange rate could produce misleading results.
CIA World Facts (1994)
This page was last up-dated:

