| Linguistics 105 * Words and Sounds |
| Lecture Number Four |
| The
Articulatory Properties of Consonants |
- Natural Classes of Consonants
(Manner and Place of Articulation)
- Stop (Occlusive) Consonants
- Stops are made by occluding the flow of air
- by pressing both lips together (bilabials): [p b]
- by pressing the tongue against
- the teeth (= dentals) [
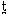
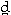 ]
]
- the alveolar ridge (= alveolars) [t d]
- the palate (= palatals) [c ™]
- the velum (= velars) [k g]
- the uvula (= uvulars) [q G]
- the teeth (= dentals) [
- by closing the glottis (vocal cords) = glottal stop [š], e.g. [Ïšo] "uh-oh"

Table 1: Stops (Occlusives) Labial Dental Alveolar Palatal Velar Uvular Glottal Voiceless p 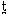
t c k q š Voiced b 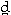
d ™ g G
- Stops are most often distinguished by voicing but in English,
they are distinguished primarily by the aspiration of voiceless
stops (except after /s/ and at the end of words).

Distribution of Aspiration in English Labial Alveolar Velar Voiceless pie [phaj] tie [thaj] kite [khajt] Voiced buy [baj] die [daj] guy [gaj] After [s] spy [spaj] sty [staj] sky [skaj] Finally map [mÀp] gnat[nÀt] knack [nÀk]
- Stops are made by occluding the flow of air
- Fricative Consonants are made by pressing the lips and the
tongue in the same places but not enough to occlude the flow of air
but to obstruct it just enough to cause friction:
- the lips (bilabial) [
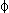 è] Spanish 'b' = [è], e.g. saber 'knowledge' ([saèer])
è] Spanish 'b' = [è], e.g. saber 'knowledge' ([saèer])
- the lips and the teeth (labiodentals) [f v]
- the tongue between the teeth (interdentals) [Ê ö], e.g. theater and this
- the teeth or alveolar ridge (alveolars) [s z]
- the palate (palatals) [Œ —], e.g. English shut and garage
- the velum (velars) [x ï], e.g. German Loch 'hole', Russian dux 'spirit'; Ukrainian golod ([ïolod]) 'hunger' vs. xolod 'cold'

Table 2: Fricatives Labial Dental Alveolar Palatal Velar Uvular Glottal Voiceless f Ê s Œ x ÷ h Voiced v ö z — ï é › - the lips (bilabial) [
- Affricate (Delayed release) Consonants. These are a combination
of a stop and a fricative.

Table 3: Affricates (Delayed Release) Labial Alveolar Palatal Velar Voiceless . ts “ . Voiced . dz ” . - Sonorant Consonants (always voiced & may be syllabic)
- Liquids: lateral [l] and circumflex [r]
- Glides: labiovelar [w] and palatal [j]
- Nasals: [m n ò ü]

Table 4: Nasals Labial Alveolar Palatal Velar Voiced m n ò ü - Additional Properties All obstruents may have additional properties
(i.e. belong to additional natural classes).
- Retroflection (Hindi):
- Palatalization (Polish, Russian): [p' b' t' d' k' g']
- Stop (Occlusive) Consonants
- Conclusions
The natural classes of consonants are based on
- Place of articulation
- lips (labials)
- teeth (dentals)
- alveolum (alveolars)
- hard palate (palatals)
- soft palate or velum (velars)
- uvula (uvulars)
- glottis (glottals)
- Manner of articulation
- occlusion (stops)
- friction (fricatives)
- occlusion + friction (affricates)
- ALSO: sonorants (nasals and liquids) and glides
- Glottal State
- voicing (vibrating the vocal folds)
- Other properties
- nasalization (opening the phraryngeal flap)
(usually considered in "Manner of Articulation") - aspiration (exhaling hard)
- sharping (Russian 'soft' consonants)
- retroflexing (curling the tongue backward)
- labialization (lip rounding)
- nasalization (opening the phraryngeal flap)
- Place of articulation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|