| Linguistics 105 * Words and Sounds |
| Lecture Number Five |
| The Articulatory Properties of Vowels |
- Natural Classes of Vowels
Vowels are classified according to the (1) advancement and (2) height of the tongue in pronunciation, (3) the tenseness of the tongue and (4) whether or not the lips are rounded during pronunciation. Finally, like consonants, vowels may be characterized by (5) nasality.
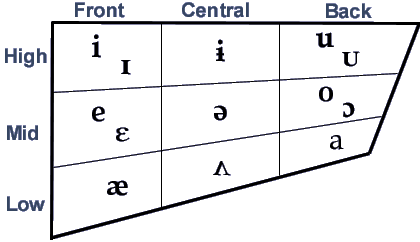
- Advancement. During the pronunciation of a vowel the tongue
may be advanced or retracted to approximately three positions: (a) the
front, (b) central or (c) back of the mouth.
([¬] = "u" in French dur)Table 1 : Advancement Front [i, °, e, ŕ, └] Central [¬, ¤, ═] Back [Ý, u, o, a, ě] - Height. The tongue may be raised (a) high, to a (b) mid position,
or remain (c) low.
Table 2 : Height High [i, °, ¬, Ý, u] Mid [e, ŕ, ¤, o, ě] Low [└, ═, a] - Tenseness. TENSE [i, e, u, o] versus LAX [°, ŕ, Ý, o] and [└, ě,]
- Labialization. ROUNDED [y, Ó, Ý, u, ě, o] (also English [r])
- Nasalization. Polish [╗ ┬]; French [│ Ă yé Óé đ]
- Suprasegmental elements: Stress, Length, Tone
- Advancement. During the pronunciation of a vowel the tongue
may be advanced or retracted to approximately three positions: (a) the
front, (b) central or (c) back of the mouth.
- Examples of English vowels
-
Lax Vowels: Stressed Unstressed Reduced ° impl■cit simpl■stic implic˙tion ŕ all§ge temp§stuous alleg˙tion └ emph˙tic fant˙stic §mphasis Ý hřodwink n§ighborhood . a demřnstrable prognřsis demonstr˙tion ě c˙use caus˙lity . ¤ conf■rm verbřse confirm˙tion ═ confrřnt umbr§lla confront˙tion Tense Vowels: Stressed Unstressed Reduced i [ij] depr§ci┌te cre˙te d§precate e [ej] expl˙in chařtic Ňxplan˙tion o [ow] invřke voc˙tion Ůnvoc˙tion u [uw] refßte ┌coust■cian rŇfut˙tion Diphthongs: Stressed Unstressed Reduced aj rec■te cit˙tion rŇcit˙tion aw devřut outs■der . ěj explřit Ňxploit˙tion . ju compßte cŢmput˙tion c■rcular
- Conclusion
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|