Turkmenistan

Geography
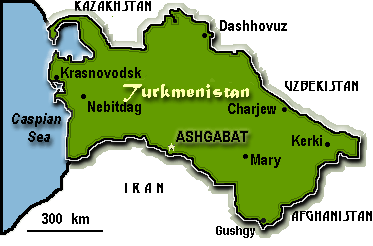
Location: Central Asia, bordering the Caspian Sea, between Iran and Uzbekistan
Area: total area 488,100 sq km land area 488,100 sq km comparative area slightly larger than California
Land boundaries: total 3,736 km, Afghanistan 744 km, Iran 992 km, Kazakhstan 379 km, Uzbekistan 1,621 km
Coastline: 0 km note Turkmenistan borders the Caspian Sea (1,768 km)
Maritime claims: landlocked, but boundaries in the Caspian Sea with Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, and Iran are under negotiations
International disputes: Russia may dispute current de facto maritime border to midpoint of Caspian Sea from shore
Climate: subtropical desert
Terrain: flat-to-rolling sandy desert with dunes rising to mountains in the south; low mountains along border with Iran; borders Caspian Sea in west
Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, coal, sulphur, salt
Land use: arable land 3% permanent crops 0% meadows and pastures 69% forest and woodland 0% other 28%
Irrigated land: 12,450 sq km (1990)
Environment:
current issues contamination of soil and groundwater with agricultural chemicals, pesticides; salinization, water-logging of soil due to poor irrigation methods; Caspian Sea pollution; diversion of a large share of the flow of the Amu Darya river into irrigation contributes to that river's inability to replenish the Aral Sea; desertification natural hazards NA international agreements party to - Ozone Layer Protection
Note: landlocked
People
Population: 3,995,122 (July 1994 est.)
Population growth rate: 2.01% (1994 est.)
Birth rate: 30.42 births/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Death rate: 7.44 deaths/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Net migration rate: -2.89 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 69.9 deaths/1,000 live births (1994 est.)
Life expectancy at birth: total population 65.14 years male 61.63 years female 68.82 years (1994 est.)
Total fertility rate: 3.77 children born/woman (1994 est.)
Nationality: noun Turkmen(s) adjective Turkmen
Ethnic divisions: Turkmen 73.3%, Russian 9.8%, Uzbek 9%, Kazakh 2%, other 5.9%
Religions: Muslim 87%, Eastern Orthodox 11%, unknown 2%
Languages: Turkmen 72%, Russian 12%, Uzbek 9%, other 7%
Literacy: age 9-49 can read and write (1970) total population 100% male 100% female 100%
Labor force: 1.573 million by occupation agriculture and forestry 44%, industry and construction 20%, other 36% (1992)
Government
Names: conventional long form none conventional short form Turkmenistan local long form Tiurkmenostan Respublikasy local short form Turkmenistan former Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic
Digraph: TX
Type: republic
Capital: Ashgabat
Administrative divisions: 5 welayatlar (singular - welayat): Ahal Welayaty (Ashgabat), Balkan Welayaty (Nebitdag), Dashhowuz Welayaty (formerly Tashauz), Lebap Welayaty (Charjew), Mary Welayaty note names in parentheses are administrative centers when name differs from welayat name
Independence: 27 October 1991 (from the Soviet Union)
National holiday: Independence Day, 27 October (1991)
Constitution: adopted 18 May 1992
Legal system: based on civil law system
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch: chief of state President Saparmurad NIYAZOV (since NA October 1990); election last held 21 June 1992 (next to be held NA 2002); results - Saparmurad NIYAZOV 99.5% (ran unopposed); note - a 15 January 1994 referendum extended NIYAZOV's term an additional five years until 2002 (99.99% approval) head of government Prime Minister (vacant); Deputy Prime Ministers Batyr SARDJAEV, Valery G. OCHERTSOV, Orazgeldi AIDOGDIEV, Djourakuli BABAKULIYEV, Rejep SAPAROV, Boris SHIKHMURADOV, Abad RIZAEVA, Yagmur OVEZOV (since NA) cabinet Council of Ministers
Legislative branch: under 1992 constitution there are two parliamentary bodies, a unicameral People's Council (Halk Maslahaty - having more than 100 members and meeting infrequently) and a 50-member unicameral Assembly (Majlis) Assembly (Majlis) elections last held 7 January 1990 (next to be held late 1994 or early 1995); results - percent of vote by party NA; seats - (175 total) elections not officially by party, but Communist Party members won nearly 90% of seats; note - seats to be reduced to 50 at next election
Judicial branch: Supreme Court
Political parties and leaders: ruling party Democratic Party (formerly Communist), chairman vacant opposition Party for Democratic Development, Durdymurat HOJA-MUKHAMMED, chairman; Agzybirlik, Nurberdy NURMAMEDOV, cochairman, Hubayberdi HALLIYEV, cochairman note formal opposition parties are outlawed; unofficial, small opposition movements exist
Member of: CIS, CSCE, EBRD, ECE, ECO, ESCAP, IBRD, ICAO, IDB, ILO, IMF, IMO, INTELSAT (nonsignatory user), IOC, ITU, NACC, OIC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WHO, WMO
Diplomatic representation in US: chief of mission Ambassador Khalil UGUR chancery 1511 K Street NW, Suite 412, Washington, DC, 20005 telephone NA
US diplomatic representation: chief of mission Ambassador Joseph S. HULINGS III embassy Yubilenaya Hotel, Ashgabat mailing address use embassy street address telephone [7] 36320 24-49-25 or 24-49-26
Economy
CIA Overview: Turkmenistan is a largely desert country with nomadic cattle raising, intensive agriculture in irrigated oases, and huge gas and oil resources. Half of its irrigated land is planted in cotton; it is the world's tenth largest producer. It also is the world's fourth largest producer of natural gas and has the fifth largest reserves. Furthermore, Turkmenistan has substantial oil resources; its two oil refineries make it an exporter of refined products. Profiting from the move toward market prices for its oil and gas resources, Turkmenistan has suffered the least economic decline of the 15 states of the former USSR. With an authoritarian ex-Communist regime in power and a tribally based social structure, Turkmenistan has taken a cautious approach to questions of economic reform, using the profits from its gas and cotton exports to sustain a generally inefficient economy. Economic restructuring and privatization have just begun, and price liberalization and price increases have been accompanied by generous wage hikes and subsidies. At the same time, Turkmenistan faces serious constraints on its gas and oil earnings because of the inability of its traditional regional customers to pay for the current level of purchases and the lack of pipeline access to hard currency markets. Faced with financial shortfalls, rampant inflation, and the desire to ensure a stable currency, the regime has become more receptive to market reforms yet still seeks to offer widespread social benefits to its population and to retain state domination over the economy.
National product: GDP - purchasing power equivalent - $13 billion (1993 estimate from the UN International Comparison Program, as extended to 1991 and published in the World Bank's World Development Report 1993; and as extrapolated to 1993 using official Turkmen statistics, which are very uncertain because of major economic changes since 1990)
National product real growth rate: 7.8% (1993 est.)
National product per capita: $3,330 (1993 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 45% per month (1993 est.)
Unemployment rate: 2.9% (1992 est.); includes only officially registered unemployed; also large number of underemployed
Budget: revenues $NA expenditures $NA, including capital expenditures of $NA
Exports: $1.2 billion to states outside the FSU (1993) commodities natural gas, cotton, petroleum products, textiles, carpets partners Ukraine, Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Georgia, Eastern Europe, Turkey, Argentina
Imports: $490 million from states outside the FSU (1993) commodities machinery and parts, grain and food, plastics and rubber, consumer durables, textiles partners Russia, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Turkey
External debt: NEGL
Industrial production: growth rate 5.3% (1993)
Electricity: capacity 2,920,000 kW production 13.1 billion kWh consumption per capita 3,079 kWh (1992)
Industries: natural gas, oil, petroleum products, textiles, food processing
Agriculture: cotton,grain, animal husbandry
Illicit drugs: illicit producer of cannabis and opium; mostly for CIS consumption; limited government eradication program; used as transshipment points for illicit drugs from Southwest Asia to Western Europe
Economic aid: recipient Turkmenistan has received about $200 million in bilateral aid credits
Currency: Turkmenistan introduced its national currency, the manat, on 1 November 1993
Exchange rates: NA
Fiscal year: calendar year
Communications
Railroads: 2,120 km; does not include industrial lines (1990)
Highways: total 23,000 km paved and gravel 18,300 km unpaved earth 4,700 km (1990)
Pipelines: crude oil 250 km; natural gas 4,400 km
Ports: inland - Krasnowodsk (Caspian Sea)
Airports: total 7 usable 7 with permanent-surface runways 4 with runways over 3,659 m 0 with runways 2,440-3,659 m 0 with runways 1,220-2,439 m 4
Telecommunications: poorly developed; only 7.5 telephone circuits per 100 persons (1991); linked by cable and microwave to other CIS republics and to other countries by leased connections to the Moscow international gateway switch; a new telephone link from Ashgabat to Iran has been established; a new exchange in Ashgabat switches international traffic through Turkey via INTELSAT; satellite earth stations - 1 Orbita and 1 INTELSAT
Defense Forces
Branches: National Guard, Republic Security Forces (internal and border troops), Joint Command Turkmenistan/Russia (Ground, Navy or Caspian Sea Flotilla, Air, and Air Defense)
Manpower availability: males age 15-49 962,987; fit for military service 787,991; reach military age (18) annually 40,079 (1994 est.)
Defense expenditures: $NA, NA% of GDP.
CIA World Facts (1994)
This page was last up-dated:
