Kazakhstan
Geography
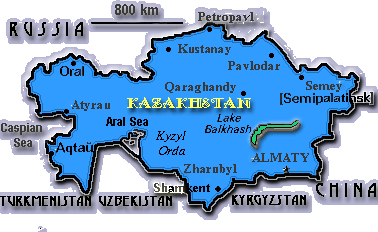
Location: Central Asia, between Russia and Uzbekistan, bordering on the Caspian Sea and the Aral SeaArea:
total area: 2,717,300 sq km
land area: 2,669,800 sq km
comparative area: slightly less than four times the size of TexasLand boundaries: total 12,012 km, China 1,533 km, Kyrgyzstan 1,051 km, Russia 6,846 km, Turkmenistan 379 km, Uzbekistan 2,203 km
Coastline: 0 km
note : Kazakhstan borders the Aral Sea (1,015 km) and the Caspian Sea (1,894 km)Maritime claims: landlocked, but borders with Russia, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan in the Caspian Sea are under negotiation at present
International disputes: Russia may dispute current de facto maritime border to midpoint of Caspian Sea from shore
Climate: continental, cold winters and hot summers, arid and semiarid
Terrain: extends from the Volga to the Altai Mountains and from the plains in western Siberia to oasis and desert in Central Asia
Natural resources: major deposits of petroleum, coal, iron ore, manganese, chrome ore, nickel, cobalt, copper, molybdenum, lead, zinc, bauxite, gold, uranium
Land use:
arable land: 15%
permanent crops: NEGL %
meadows and pastures: 57%
forest and woodland: 4%
other: 24%Irrigated land: 23,080 sq km (1990)
Environment:
current issues: radioactive or toxic chemical sites associated with its former defense industries and test ranges are found throughout the country and pose health risks for humans and animals; industrial pollution is severe in some cities; because the two main rivers which flowed into the Aral Sea have been diverted for irrigation, it is drying up and leaving behind a harmful layer of chemical pesticides and natural salts; these substances are then picked up by the wind and blown into noxious dust storms; pollution in the Caspian Sea; soil pollution from overuse of agricultural chemicals and salinization from faulty irrigation practices
natural hazards: NA
international agreements : signed, but not ratified - Biodiversity, Climate ChangeNote: landlocked
People
Population: 17,267,554 (July 1994 est.)
Population growth rate: 0.64% (1994 est.)
Birth rate: 19.4 births/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Death rate: 7.93 deaths/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Net migration rate: -5.09 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 40.9 deaths/1,000 live births (1994 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population : 68.04 years
male: 63.39 years
female: 72.93 years (1994 est.)Total fertility rate: 2.44 children born/woman (1994 est.)
Nationality:
noun : Kazakhstani(s)
adjective: KazakhstaniEthnic divisions: Kazakh (Qazaq) 41.9%, Russian 37%, Ukrainian 5.2%, German 4.7%, Uzbek 2.1%, Tatar 2%, other 7.1% (1991 official data)
Religions: Muslim 47%, Russian Orthodox 44%, Protestant 2%, other 7%
Languages: Kazakh (Qazaqz) official language spoken by over 40% of population, Russian (language of interethnic communication) spoken by two-thirds of population and used in everyday business
Literacy: age 9-49 can read and write (1970)
total population: 100%
male: 100%
female: 100%Labor force: 7.356 million
by occupation: industry and construction 31%, agriculture and forestry 26%, other 43% (1992)
Government
Names:
conventional long form: Republic of Kazakhstan
conventional short form: Kazakhstan
local long form : Kazakhstan Respublikasy
local short form: none
former: Kazakh Soviet Socialist RepublicDigraph: KZ
Type: republic
Capital: Almaty
Administrative divisions: 19 oblystar (singular - oblys) and 1 city (qalalar, singular - qala)*; Almaty*, Almaty Oblysy, Aqmola Oblysy, Aqtobe Oblysy, Atyrau Oblysy, Batys Qazaqstan Oblysy (Oral), Kokshetau Oblysy, Mangghystau Oblysy, Ongtustik Qazaqstan Oblysy (Shymkent), Qaraghandy Oblysy, Qostanay Oblysy, Qyzylorda Oblysy, Pavlodar Oblysy, Semey Oblysy, Shyghys Qazaqstan Oblysy (Oskemen; formerly Ust'-Kamenogorsk), Soltustik Qazaqstan Oblysy (Petropavl), Taldyqorghan Oblysy, Torghay Oblysy, Zhambyl Oblysy, Zhezqazghan Oblysy
note: names in parentheses are administrative centers when name differs from oblys nameIndependence: 16 December 1991 (from the Soviet Union)
National holiday: Independence Day, 16 December (1991)
Constitution: adopted 28 January 1993
Legal system: based on civil law system
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state : President Nursultan A. NAZARBAYEV (since NA April 1990); Vice President Yerik ASANBAYEV (since 1 December 1991); election last held 1 December 1991 (next to be held NA 1995); percent of vote by party NA; Nursultan A. NAZARBAYEV ran unopposed
head of government: Prime Minister Sergey TERESHCHENKO (since 14 October 1991); First Deputy Prime Minister Arkezhan KAZHEGELDIN (since NA November 1993)
cabinet: Council of Ministers; appointed by the prime ministerLegislative branch: unicameral
Supreme Council: elections last held 7 March 1994 (next to be held NA 1999); results - percent of vote by party NA; seats - (177 total) Union Peoples' Unity of Kazakhstan 33, Federation of Trade Unions of the Republic of Kazakhstan 11, People's Congress of Kazakhstan Party 9, Socialist Party of Kazakhstan 8, Peasant Union of the Republic Kazakhstan 4, Social Movement "LAD" 4, Organization of Veterans 1, Union of Youth of Kazakhstan 1, Democratic Committee for Human Rights 1, Association of Lawyers of Kazakhstan 1, International Public Committee "Aral-Asia-Kazakhstan" 1, Congress of Entrepreneurs of Kazakhstan 1, Deputies of the 12th Supreme Soviet 40, independents 62Judicial branch: Supreme Court
Political parties and leaders: Peoples Unity Movement (PUU), Kuanysh SULTANOV, chairman; Peoples Congress, Olzhas SULEYMENOV, chairman; Kazakhstan Socialist Party (SPK; former Communist Party), Piotr SVOIK, co-chairman; Republican Party (Azat), Kamal ORMANTAYEV, chairman; Democratic Progress (Russian) Party, Alexandra DOKUCHAYEVA, chairman; Union Peoples' Unity of Kazakhstan (SNEK); Federation of Trade Unions of the Republic of Kazakhstan; Peasant Union of the Republic Kazakhstan; Social Movement LAD (Slavic Rebirth Society), V. MIKHAYLOV, chairman; Union of Youth of Kazakhstan; Democratic Committee for Human Rights; Association of Lawyers of Kazakhstan; International Public Committee "Aral-Asia-Kazakhstan"; Congress of Entrepreneurs of Kazakhstan; Deputies of the 12th Supreme Soviet
Other political or pressure groups: Independent Trade Union Center (Birlesu; an association of independent trade union and business associations), Leonid SOLOMIN, president
Member of: CCC, CIS, CSCE, EBRD, ECO, ESCAP, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IFC, ILO, IMF, INTELSAT (nonsignatory user), INTERPOL, IOD, NACC, OIC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WHO, WMO
Diplomatic representation in US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Tuleutai SULEYMENOV
chancery: 3421 Massachusetts Avenue, NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: (202) 333-4504/7
FAX: (202) 333-4509US diplomatic representation:
chief of mission: Ambassador William H. COURTNEY
embassy: 99/97 Furmanova Street, Almaty, Republic of Kazakhstan 480012
mailing address: American Embassy Almaty, c/o Department of State, Washington, DC, 20521-7030
telephone: (7) (3272) 63-17-70, 63-24-26, 63-28-80, 63-34-05
FAX: (7) (3272)63-38-83
Economy
Overview: Kazakhstan, the second largest of the former Soviet states in territory, possesses vast oil, coal, rare metals, and agricultural resources. While the economy is gradually making the transition from a Soviet command system to a market system, strong elements of state control persist including government ownership of most economic assets and a continued system of mandatory state procurement for the key products such as grain and energy; likewise, agriculture remains largely collectivized. On the other hand, new businesses are forming rapidly, the economy is opening to foreign investment, and 12% of state-owned commercial enterprises have been privatized. In 1993, a three-year industrial privatization program was launched; an independent currency was successfully introduced; and two large joint ventures were established with western oil companies. These far-reaching structural transformations have resulted in a cumulative decline in national income of more than 30% since 1990. Loose monetary policies have kept the inflation rate high, averaging 28% per month for 1993 and accelerating at the end with the disruption caused by a new currency. Since the introduction of its independent currency in November 1993, the government has renewed its commitment to fiscal discipline and accelerating economic reform. However, growing economic hardship and rising ethnic tensions between Kazakhs and Russians over the division of economic assets will likely lead to strong pressure to backtrack.
National product: GDP - purchasing power equivalent - $60.3 billion (1993 estimate from the UN International Comparison Program, as extended to 1991 and published in the World Bank's World Development Report 1993; and as extrapolated to 1993 using official Kazakhstani statistics, which are very uncertain because of major economic changes since 1990)
National product real growth rate: -13% (1993 est.)
National product per capita: $3,510 (1993 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 28% per month (1993)
Unemployment rate: 0.6% includes only officially registered unemployed; also large numbers of underemployed workers
Budget:
revenues: $NA
expenditures: $NA, including capital expenditures of $1.76 billion (1991 est.)Exports: $1.3 billion to outside the FSU countries (1993)
commodities : oil, ferrous and nonferrous metals, chemicals, grain, wool, meat (1992)
partners: Russia, Ukraine, UzbekistanImports: $358.3 million from outside the FSU countries (1993)
commodities: machinery and parts, industrial materials, oil and gas (1992)
partners: Russia and other former Soviet republics, ChinaExternal debt: $1.5 billion debt to Russia
Industrial production: growth rate -16% (1993)
Electricity:
capacity: 19,135,000 kW
production: 81.3 billion kWh
consumption per capita : 4,739 kWh (1992)Industries: extractive industries (oil, coal, iron ore, manganese, chromite, lead, zinc, copper, titanium, bauxite, gold, silver, phosphates, sulfur), iron and steel, nonferrous metal, tractors and other agricultural machinery, electric motors, construction materials
Agriculture: accounts for almost 40% of net material product; employs about 26% of the labor force; grain, mostly spring wheat; meat, cotton, wool
Illicit drugs: illicit cultivation of cannabis and opium poppy; mostly for CIS consumption; limited government eradication program; used as transshipment point for illicit drugs to Western Europe and North America from Central and Southwest Asia
Economic aid:
recipient: approximately $1 billion in foreign credits to become available in 1994Currency: national currency the tenge introduced on 15 November 1993
Exchange rates: NA
Fiscal year: calendar year
Communications
Railroads: 14,460 km (all 1.520-meter gauge); does not include industrial lines (1990)
Highways:
total: 189,000 km
paved and graveled: 108,100 km
unpaved: earth 80,900 km (1990)Inland waterways: Syrdariya River, Ertis River
Pipelines: crude oil 2,850 km; refined products 1,500 km; natural gas 3,480 km (1992)
Ports: inland - Atyrau (formerly Gur'yev; on Caspian Sea)
Airports:
total: 365
usable: 152
with permanent-surface runways: 49
with runways over 3,659 m : 8
with runways 2,440-3,659 m: 38
with runways 1,220-2,439 m : 71Telecommunications: telephone service is poor, with only about 17 telephones for each 100 persons in urban areas and 7.6 telephones per 100 persons in rural areas; of the approximately 2.2 million telephones, Almaty has 184,000; broadcast receivers - TVs 4,750,000, radios 4,088,000, radio receiver systems with multiple speakers for program diffusion 6,082,000; international traffic with other former USSR republics and China carried by landline and microwave, and with other countries by satellite and through 8 international telecommunications circuits at the Moscow international gateway switch; satellite earth stations - INTELSAT and Orbita (TV receive only); new satellite ground station established at Almaty with Turkish financial help (December 1992) with 2500 channel band width
Defense Forces
Branches: Army, National Guard, Security Forces (internal and border troops)
Manpower availability: males age 15-49 4,432,716; fit for military service 3,554,209; reach military age (18) annually 154,989 (1994 est.)
Defense expenditures: 69,326 million rubles, NA% of GDP (forecast for 1993); note - conversion of the military budget into US dollars using the current exchange rate could produce misleading results.
CIA Data Files (1994)
This page was last up-dated: